Research
 Biogenic avenues towards infection and antiinflammatory therapy
Biogenic avenues towards infection and antiinflammatory therapy
The combination of incorrect and overly frequent application of antibiotics and insufficient hygiene measures in hospitals leads to a worldwide rise in the number of resistant bacteria for which ever less effective therapies exist. At the Chair for Pharmaceutical Biology intelligent mechanisms of action and nano-systems that transport known antibiotics to infected sites in the human body are explored. We apply state-of-the-art biomimetic systems that utilise mechanisms found in nature or are derived from them. This allows for an effective control of pathogenic bacteria with minimal adverse effects. … >
 We are member of FAU Research Centre New Bioactive Compounds (NeW)
We are member of FAU Research Centre New Bioactive Compounds (NeW)
Was macht eigentlich ein pharmazeutischer Biologe? Our research in a nutshell

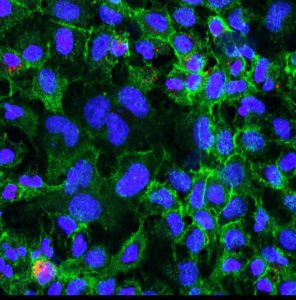
Extracellular vesicles
Our focus is on the characterisation of extracellular vesicles (EVs) as natural conveyers of cellular information. EVs are nanoparticles of 50-200 nm in size that are produced naturally by virtually all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. EVs consists of a lipid double layer, carry signal molecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids (e.g. microRNA), and are very efficient cell-cell communicators that migrate from one cell type to another, interact with the target cell by means of their surface and membrane proteins and thus transfer signal molecules in a highly specific manner. … >
————-
Vilhena lab -Bacterial Interface Dynamics
Our lab investigates the dynamic interactions between Streptococcus pneumoniae and its environment, with a specific focus on the formation and function of bacterial extracellular vesicles (EVs). EVs are not only essential for intercellular communication but also play crucial roles in infection and immune evasion. Investigating their biogenesis will facilitate downstream bioengineering applications. >